Doubly Linked List
A Doubly Linked List is a more sophisticated data structure compared to a Singly Linked List. In a Doubly Linked List, each node contains three fields: data, a pointer to the next node, and a pointer to the previous node. This structure allows for traversal in both directions—from the head (the first node) to the tail (the last node), and vice versa.
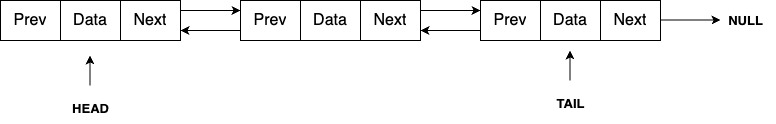
Structure of a Doubly Linked List
In Go, a Doubly Linked List is typically implemented using two structs: one to represent the individual nodes of the list and another to manage the list as a whole.
Node struct
The Node struct holds the data and has two references: one (next) to the next node in the list and one (prev) to the previous node.
type Node struct {
data int
next *Node
prev *Node
}
LinkedList struct
The LinkedList struct manages the entire list and typically contains a reference to the head node.
type LinkedList struct {
head *Node
}
Basic Operations on a Doubly Linked List
To work with a Doubly Linked List, we need to define several essential operations such as inserting a node, deleting a node, and printing the list's contents. Below is an outline of these operations using pseudo-code in Go.
package main
// import necessary packages
type Node struct {
data int
next *Node
prev *Node
}
type LinkedList struct {
head *Node
}
func (list *LinkedList) insertNode(data int) {
// Code to insert a node into the list
}
func (list *LinkedList) deleteNode(val int) {
// Code to delete a node from the list
}
func (list *LinkedList) printList() {
// Code to print all nodes in the list
}
func main(){
list := LinkedList{}
list.insertNode(10)
list.deleteNode(10)
list.insertNode(20)
list.insertNode(30)
list.printList()
}
Implementing the Operations
Let's dive into the actual implementation of the insertNode, deleteNode, and printList functions:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
// Node represents an element in the doubly linked list
type Node struct {
data int
next *Node
prev *Node
}
// LinkedList represents the doubly linked list
type LinkedList struct {
head *Node
}
// Insert a new node at the end of the list
func (l *LinkedList) insertNode(data int) {
// Create a new node with the provided data
node := &Node{data: data}
// If the list is empty, set the new node as the head
if l.head == nil {
l.head = node
return
}
// Traverse the list to find the last node
ptr := l.head
for ptr.next != nil {
ptr = ptr.next
}
// Set the new node as the next node of the last node and update the previous pointer of the new node
node.prev = ptr
ptr.next = node
}
// Delete a node by value from the list
func (l *LinkedList) deleteNode(data int) {
// Check if the list is empty
if l.head == nil {
fmt.Println("List is empty")
return
}
// Pointer to traverse the list
ptr := l.head
// Check if the node to delete is the head node
if ptr.data == data {
l.head = ptr.next
if l.head != nil {
l.head.prev = nil // Update the previous pointer of the new head
}
return
}
// Traverse the list to find the node with the matching data
for ptr != nil && ptr.data != data {
ptr = ptr.next
}
// If the node was not found
if ptr == nil {
fmt.Println("Number not found")
return
}
// If the node to delete is the last node
if ptr.next == nil {
ptr.prev.next = nil
} else {
// If the node to delete is in the middle, update the pointers of the neighboring nodes
ptr.next.prev = ptr.prev
ptr.prev.next = ptr.next
}
}
// Print all nodes in the list
func (l *LinkedList) printNodes() {
// Pointer to traverse the list
ptr := l.head
var list string
// Traverse and concatenate the data of each node to the list string
for ptr != nil {
list += strconv.Itoa(ptr.data) // Convert integer data to string and add to the list
// If not the last node, add an arrow to the string
if ptr.next != nil {
list += "--->"
}
ptr = ptr.next
}
// Print the final concatenated string representing the linked list
fmt.Println(list)
}
// main function to demonstrate the linked list operations
func main() {
// Create an empty linked list
l := LinkedList{}
// Insert nodes into the linked list
l.insertNode(1)
l.insertNode(2)
l.insertNode(3)
l.insertNode(4)
// Print the linked list
l.printNodes() // Output: 1--->2--->3--->4
// Delete a node from the linked list
l.deleteNode(1)
l.printNodes() // Output: 2--->3--->4
// Try to delete a non-existent node
l.deleteNode(10) // Output: Number not found
}
This Go code demonstrates how to manage a Doubly Linked List by inserting and deleting nodes, as well as printing the list’s contents.
For a more detailed exploration and code examples, you can check out my work on GitHub: Doubly Linked List in Go.